Productivity: More with Less by Better
Available resources are scarce. To sustain our society's income and living standards in a world with ecological and demographic change, we need to make smarter use of them.
Dossier

In a nutshell
Nobel Prize winners Paul Samuelson and William Nordhaus state in their classic economics textbook: Economics matters because resources are scarce. Indeed, productivity research is at the very heart of economics as it describes the efficiency with which these scarce resources are transformed into goods and services and, hence, into social wealth. If the consumption of resources is to be reduced, e. g., due to ecological reasons, our society’s present material living standards can only be maintained by productivity growth. The aging of our society and the induced scarcity of labour is a major future challenge. Without productivity growth a solution is hard to imagine. To understand the processes triggering productivity growth, a look at micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments is indispensable.
Our experts

Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-708 Request per E-Mail
President
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-700 Request per E-MailAll experts, press releases, publications and events on “Productivity”
Productivity is output in relation to input. While the concept of total factor productivity describes how efficiently labour, machinery, and all combined inputs are used, labour productivity describes value added (Gross Domestic Product, GDP) per worker and measures, in a macroeconomic sense, income per worker.
Productivity Growth on the Slowdown
Surprisingly, despite of massive use of technology and rushing digitisation, advances in productivity have been slowing down during the last decades. Labour productivity growth used to be much higher in the 1960s and 1970s than it is now. For the G7 countries, for example, annual growth rates of GDP per hour worked declined from about 4% in the early 1970s to about 2% in the 1980s and 1990s and then even fell to about 1% after 2010 (see figure 1).
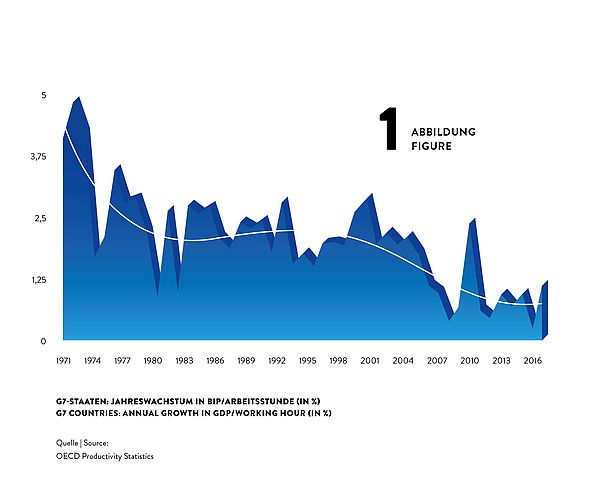
This implies a dramatic loss in potential income: Would the 4% productivity growth have been sustained over the four and a half decades from 1972 to 2017, G7 countries’ GDP per hour would now be unimaginable 2.5 times as high as it actually is. What a potential to, for instance, reduce poverty or to fund research on fundamentals topics as curing cancer or using fusion power!
So why has productivity growth declined dramatically although at the same time we see, for instance, a boom in new digital technologies that can be expected to increase productivity growth? For sure, part of the decline might be spurious and caused by mismeasurement of the contributions of digital technologies. For instance, it is inherently difficult to measure the value of a google search or another video on youtube. That being said, most observers agree that part of the slowdown is real.
Techno-Pessimists and Techno-Optimists
Techno-pessimists say, well, these new technologies are just not as consequential for productivity as, for instance, electrification or combustion engines have been. Techno-optimists argue that it can take many years until productivity effects of new technologies kick in, and it can come in multiple waves. New technology we have now may just be the tools to invent even more consequential innovations in the future.
While this strand of the discussion is concerned with the type of technology invented, others see the problem in that inventions nowadays may diffuse slowly from technological leaders to laggards creating a wedge between few superstar firms and the crowd (Akcigit et al., 2021). Increased market concentration and market power by superstar firms may reduce competitive pressure and the incentives to innovate.
Finally, reduced Schumpeterian business dynamism, i.e. a reduction in firm entry and exit as well as firm growth and decline, reflects a slowdown in the speed with which production factors are recombined to find their most productive match.
While the explanation for and the way out of the productivity puzzle are still unknown, it seems understood that using granular firm level data is the most promising path to find answers.
What are the Origins of Productivity Growth?
Aggregate productivity growth can originate from (i) a more efficient use of available inputs at the firm level as described above or (ii) from an improved allocation of resources between firms.
Higher efficiency at the firm level captures, e.g., the impact of innovations (Acemoglu et al., 2018) or improved firm organisation (management) (Heinz et al., 2020; Müller und Stegmaier, 2017), while improved factor allocation describes the degree of which scarce input factors are re-allocated from inefficient to efficient firms (‘Schumpeterian creative destruction’) (Aghion et al., 2015; Decker et al., 2021).
Most economic processes influence the productivity of existing firms and the growth and the use of resources of these firms and their competitors as well. The accelerated implementation of robotics in German plants (Deng et al., 2020), the foreign trade shocks induced by the rise of the Chinese economy (Bräuer et al., 2019), but also the COVID-19 pandemic, whose consequences are still to evaluate (Müller, 2021) not only effects on productivity and growth of the firms directly affected but at the same time may create new businesses and question existing firms.
While productivity can be measured at the level of aggregated sectors or economies, micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments are indispensable to study firm organisation, technology and innovation diffusion, superstar firms, market power, factor allocation and Schumpeterian business dynamism. The IWH adopts this micro approach within the EU Horizon 2020 project MICROPROD as well as with the CompNet research network.
As “creative destruction” may also negatively affect the persons involved (e. g., in the case of layoffs, Fackler et al., 2021), the IWH analyses the consequences of bankruptcies in its Bankruptcy Research Unit and looks at the implications of creative destruction for the society, e. g., within a project funded by Volkswagen Foundation searching for the economic origins of populism and in the framework of the Institute for Research on Social Cohesion.
Publications on “Productivity”

Die funktionale Spezialisierung Deutschlands — Eine Ost-West-Perspektive auf das Verarbeitende Gewerbe
in: Contribution to IWH Volume, Festschrift für Gerhard Heimpold, IWH 2020
Abstract
Was treibt regionale Entwicklung? Warum wachsen einige Regionen schneller als andere? Diese Fragen stehen im Mittelpunkt regionalökonomischer Forschung. Einen besonderen Anwendungsfall stellen die ökonomischen Anpassungsprozesse im Gefolge der Wiederherstellung der Deutschen Einheit dar. Nach einem fulminanten Start in der ersten Hälfte der 1990er Jahre hat sich der Aufholprozess seit Mitte der 1990er Jahre verlangsamt und kommt seitdem nur noch in sehr kleinen Schritten voran. Im Jahr 2017 betrug die Produktivität Ostdeutschlands (mit Berlin) 82% des westdeutschen Niveaus. Über die Ursachen dieses Rückstands gibt es intensive Diskussionen.

Wissens- und Technologietransfer und wissensbasierte Wirtschaftsentwicklung — ein Weg zur Förderung des wirtschaftlichen Aufholprozesses in Ostdeutschland?
in: Contribution to IWH Volume, Festschrift für Gerhard Heimpold, IWH 2020
Abstract
Der wirtschaftliche Transformations- und Aufholprozess in Ostdeutschland seit 1990 hat sich gemäß verschiedenen Analysen und Publikationen nicht zuletzt des Leibniz-Instituts für Wirtschaftsforschung Halle in einer deutlichen Steigerung der Arbeitsproduktivität niedergeschlagen: Während in Ostdeutschland 1991 nur rund 45% des Bruttoinlandsprodukts Westdeutschlands pro Erwerbstätigen erwirtschaftet wurden, so stieg dieser Wert bis 2018 auf 83%. Die Erklärungen für diese noch immer bestehende ostdeutsche „Produktivitätslücke“ sind multifaktoriell und werden etwa in fehlenden Headquarterfunktionen, der Betriebsstruktur mit wenigen Großbetrieben, der auf Arbeitsplätze fokussierten Investitionsförderung, siedlungsstrukturellen Unterschieden, einem zunehmenden Fachkräftemangel und nicht zuletzt niedrigeren Preisen für in Ostdeutschland produzierte Güter und Dienstleistungen gesucht. Folglich braucht es auch in vielen Wirtschafts- und Lebensbereichen und auf allen Ebenen Strategien und Maßnahmen. Während eine Angleichung der Unternehmensstrukturen hinsichtlich Branchen, Größenstrukturen oder Funktionen, wie etwa der Durchführung von Forschung und Entwicklung (FuE) in Ostdeutschland, sowohl mittels Unternehmensverlagerungen als auch Neugründungen von Unternehmen als Maßnahmen mit langfristiger Wirkung betrachtet werden, wurde und wird große Hoffnung in den öffentlichen Bildungs- und Forschungssektor und seinen Beitrag zu einer wissens- und technologiegestützten Entwicklung gesetzt.

Why Do Workers at Larger Firms Outperform?
in: Working Paper, 2020
Abstract
Workers at larger firms outperform on average. For example, equity analysts working for more reputable brokerage firms produce more accurate earnings forecasts. Analysts employed by the highest ranked brokerages are about 6% more accurate than those employed by the lowest ranked brokerages, which is equivalent to an advantage of 17.5 years of more experience. This outperformance is driven by two significant effects: more reputable firms provide more resources that improve analysts' forecasting ability (influence), while more reputable firms also attract more talented candidates (sorting). We estimate a two-sided matching model to disentangle these two effects. We find that the direct influence effect accounts for 73% of the total impact while the sorting effect accounts for the remaining 27%.
Aktuelle Trends: Entwicklung der Firmengründungen in Deutschland
in: Wirtschaft im Wandel, No. 1, 2020
Abstract
Das Produktivitätswachstum in entwickelten Volkswirtschaften hat sich in den letzten Jahren deutlich verlangsamt. Ein Indikator für die wirtschaftliche Dynamik in einer Volkswirtschaft ist die Firmengründungsaktivität. Wenn neue Ideen entstehen, kann dies in eine zunehmende Gründungsaktivität münden und so positiv auf die Produktivitätsentwicklung wirken.

Zu den betrieblichen Effekten der Investitionsförderung im Rahmen der deutschen Regionalpolitik
in: Wirtschaft im Wandel, No. 1, 2020
Abstract
Die Wirtschaft in den Industrieländern unterliegt einem ständigen Anpassungsdruck. Wichtige aktuelle Treiber des Strukturwandels sind vor allem die Globalisierung, der technologische Fortschritt (insbesondere durch Digitalisierung und Automatisierung), die Demographie (durch Alterung und Schrumpfung der Bevölkerung) und der Klimawandel. Von diesem Anpassungsdruck sind jedoch die Regionen in Deutschland sehr unterschiedlich betroffen. Regionalpolitik verfolgt das Ziel, Regionen bei der Bewältigung des Strukturwandels zu unterstützen. Ein besonderer Fokus liegt dabei auf Regionen, die ohnehin durch Strukturschwächen gekennzeichnet sind. Die aktuelle Regionalförderung in Deutschland basiert im Wesentlichen auf der Förderung von Investitionen von Betrieben und Kommunen. Die Evaluierung dieser Programme muss integraler Bestandteil der Regionalpolitik sein – schließlich stellt sich immer die Frage nach einer alternativen Verwendung knapper öffentlicher Mittel. Eine Pilotstudie für Sachsen-Anhalt zeigt, dass die im Rahmen der Regionalpolitik gewährten Investitionszuschüsse einen positiven Effekt auf Beschäftigung und Investitionen der geförderten Betriebe haben; bei den Investitionen allerdings nur für die Dauer des Projekts. Effekte der Förderung auf Umsatz und Produktivität von Betrieben in Sachsen-Anhalt waren nicht nachweisbar.



